AI is no longer just for tech giants. It’s a growth engine for startups, enterprises, and everyone in between. What was once experimental is now essential for faster development, automation, and user engagement. From smarter decisions to real-time insights, AI is powering the next wave of business innovation.
In 2026, adoption has surged. Over 800 million people use AI tools weekly, with 10 million+ paying for premium services. More than 92% of Fortune 500 companies now integrate AI through cloud platforms. Monthly traffic on major AI platforms has reached nearly 4 billion visits. These trends show one thing clearly: AI is no longer being built in-house; it’s being delivered as a service, fueling everything from customer support to AI trading and real-time decision-making.
What is AI as a Service (AIaaS)?
AI as a Service (AIaaS) is a cloud-based model that gives companies instant access to advanced AI tools without building them from scratch. For many AI startups, this means skipping the heavy costs and long timelines of custom development. Instead, they can plug into pre-trained models and APIs to test, build, and scale faster.
AI as a service for businesses makes adoption simple. Teams can use powerful features like natural language processing, forecasting, or automation without needing a full team of data scientists. It’s pay-as-you-go, managed in the cloud, and ready to integrate with websites, apps, or internal systems in just a few clicks.
How AI as a Service Works?
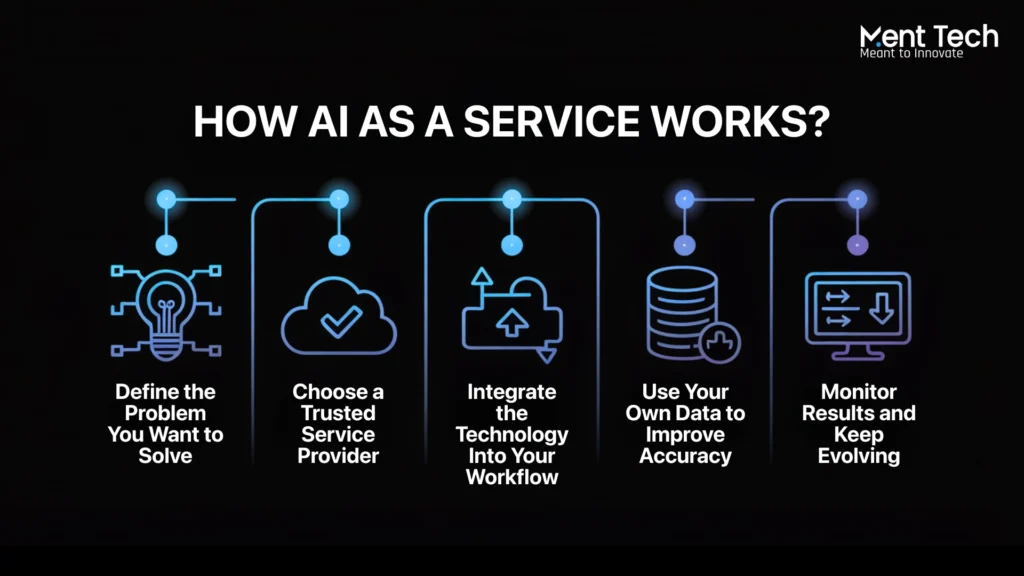
You are no longer required to construct intelligent systems from the foundation. Instead of spending months developing, training, and deploying models, businesses now plug into ready-made tools through subscription-based platforms. This is how the process unfolds.
Step 1: Define the Problem You Want to Solve
Every powerful system starts with a clear objective. The goal could be to improve customer conversations, classify documents, predict future sales, or reduce fraud. When the use case is well defined, selecting the right service becomes easier.
Step 2: Choose a Trusted Service Provider
Not all platforms offer the same features. Some focus on text understanding, others on vision or prediction. Explore providers that align with your goal, budget, and in-house capabilities.
Step 3: Integrate the Technology Into Your Workflow
Most providers offer access through plug-and-play interfaces or ready-to-use code blocks. With just a few lines, you can connect your product to their system and start receiving responses instantly.
Step 4: Use Your Own Data to Improve Accuracy
Prebuilt services often perform well from the start. But if you want results that reflect your unique product or audience, feeding your own data is the next step
Step 5: Monitor Results and Keep Evolving
Once live, the service begins powering your product in real time. You can track usage, review responses, and make changes through dashboards provided by the platform.
Types of AI as a Service You Can Use Today
AI as a Service is not a single tool. It includes a wide variety of intelligent features, each solving different business problems. From conversation systems to real-time analytics, these categories help teams deliver better products without building complex infrastructure.
1. Virtual Assistants and Chat Systems
These tools help businesses respond to users faster and more efficiently. They simulate conversations, handle questions, and reduce the load on support teams. Many come with language understanding features and can be embedded into websites, apps, or even messaging platforms.
Use cases:
- Customer support that works round the clock
- Onboarding new users through guided steps
- Gathering product feedback automatically
2. Learning Models for Prediction and Analysis
These services process your data and return patterns, trends, or predictions. Businesses use them to forecast demand, identify risks, or personalize experiences. These systems improve over time and adjust as new information becomes available.
Use cases:
- Predicting user churn or purchase intent
- Scoring leads in sales tools
- Monitoring transactions for irregular behavior
3. Image and Video Processing Tools
Vision-based services help analyze visual content. These tools detect faces, read signs, count objects, or flag items in photos and videos. Companies in retail, logistics, security, and manufacturing rely on these services to extract insights from visuals.
Use cases:
- Verifying identity in onboarding flows
- Tagging products in large media libraries
- Watching footage to detect safety violations
4. Text and Document Processing Systems
These tools work with large volumes of text. They summarize content, extract key data, translate between languages, or classify messages by urgency. Legal, healthcare, and finance teams use these to improve accuracy and reduce review time.
Use cases:
- Sorting legal documents by category
- Translating and structuring reports
- Highlighting key points in long-form content
5. Task-Specific Smart Tools
Some services are designed for one core function. This could be analyzing sentiment, generating ideas, writing short product blurbs, or summarizing user feedback. These tools are quick to deploy and work well in support, marketing, or product development teams.
Use cases:
- Scanning reviews to detect user pain points
- Writing product descriptions for online listings
- Flagging complaints that need urgent attention

Why Businesses are Choosing AI as a Service in 2026?
The rapid growth of AI as a service is driven by results. Businesses are turning to this model because it offers faster development, lower costs, and fewer technical barriers. In a competitive world, including emerging areas like AI in Web3, these advantages help companies build smarter without slowing down.
Here are the most important reasons teams are adopting this approach right now.
1. Faster Product Delivery
Speed is a competitive advantage. AI as a Service allows businesses to release new features in days instead of months. Since most platforms offer ready-to-use models and tools, teams can skip the time-consuming setup and get straight to building.
Shorter release cycles mean better user feedback, faster improvements, and quicker returns.
2. Lower Development Costs
Custom intelligence systems can drain time and money. AI as a Service eliminates the need for large upfront investments by offering usage-based pricing. Teams only pay for what they use. This model makes it easier to experiment without long-term financial commitments.
It is a practical way to test ideas without draining budgets.
3. Easier to Use for Non-Technical Teams
Many platforms offer no-code or low-code tools that do not require engineering support. This allows product managers, designers, and marketers to contribute directly. Teams across the company can now explore and build without relying on developers.
The process becomes collaborative instead of restricted to technical teams.
4. Built to Grow With You
Service providers handle the scaling in the background. If your product grows from a hundred users to a million, the system expands automatically. This flexibility removes infrastructure limits and supports long-term growth.
You stay focused on building while the platform handles expansion.
5. Strong Security and Compliance Standards
Top providers follow strict compliance rules and offer end-to-end encryption. Businesses can rely on pre-built security protocols without needing to create custom protection layers. This is especially useful for companies in finance, healthcare, or enterprise software.
Security becomes a shared responsibility with expert systems in place.
Challenges and Limitations of AI as a Service
While the benefits are clear, AI as a service comes with certain limitations. Businesses need to weigh the tradeoffs before choosing this model. Working with Adaptive AI Solutions helps teams plan ahead and maximize platform value.
Here are the most common concerns that come up with AI as a Service.
1. Long-Term Costs Can Add Up
At first, usage-based pricing feels efficient. You only pay for what you use. But as product traffic increases, so do the bills. For growing teams, what starts as a cost-saving solution can turn into a significant recurring expense. It is important to track usage closely and forecast spending based on expected growth.
Teams must compare the cost of AI as a Service to the cost of building in-house as usage scales.
2. Limited Visibility Into How Results Are Generated
Most platforms do not reveal how their models work under the hood. You get results, but not the logic behind them. This makes it difficult to explain how outputs were produced, especially when transparency is needed for regulation or client reporting.
Without full control, businesses must rely on the platform’s internal standards and documentation.
3. Vendor Lock-In and Migration Friction
Switching from one provider to another is not always simple. Once a product is integrated with a specific platform, moving to a new service often requires rewriting code, retraining systems, or changing workflows. This lock-in can limit flexibility in the future.
Careful planning during early stages helps reduce dependency and keep options open.
4. Data Security and Privacy Risks
Using AI as a Service often means sending sensitive data to third-party servers. While top providers offer strong encryption and privacy controls, businesses are still responsible for what happens to the data. Industries like finance, healthcare, and legal must review compliance before integrating external systems.
Data handling agreements and security reviews should be in place before deployment.
5. Generalized Models May Miss the Mark
Prebuilt models are designed to work across many industries. This makes them easy to use, but also limits how specific or fine-tuned they can be. A tool trained on general text might miss context in a legal document or deliver weak results in a medical application.
In many cases, adding your own data or building hybrid workflows is the best way to improve accuracy.
How Different Industries Use AI as a Service?
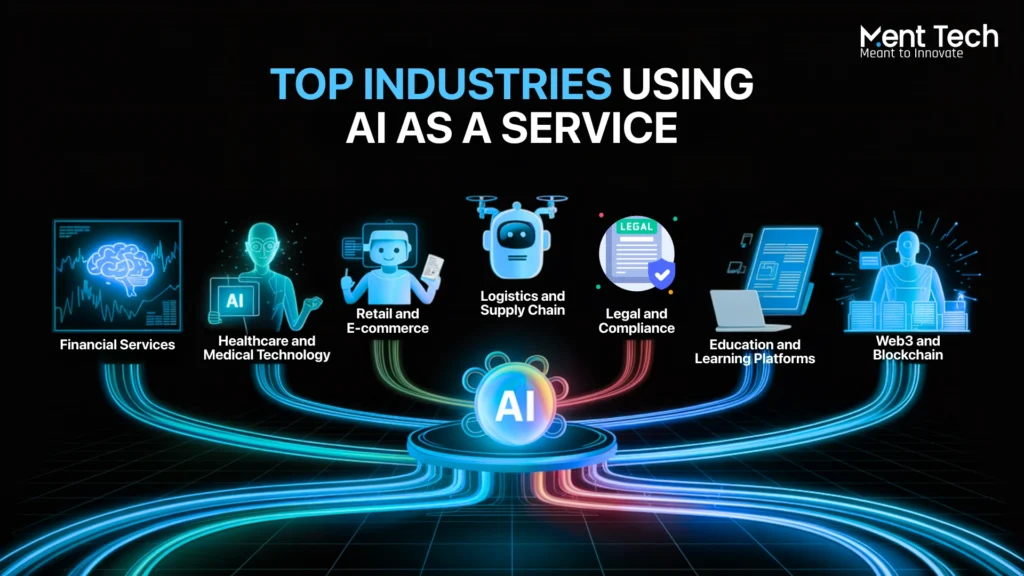
1. Financial Services
Banks and fintech companies use AIaaS to detect fraud, assess credit risk, automate compliance, and enhance financial advisory support.
2. Healthcare and Medical Technology
Hospitals and healthtech startups apply intelligent systems for diagnostics support, patient triage, appointment scheduling, and secure records handling.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Online and offline retailers use smart recommendation engines, automated customer support, and behavior analysis tools to increase sales and satisfaction.
4. Logistics and Supply Chain
Transport companies and fulfillment centers use forecasting tools and route optimization systems to reduce delays and improve delivery accuracy.
5. Legal and Compliance
Law firms and contract-heavy businesses use document review engines to analyze, summarize, and classify legal content with greater speed and accuracy.
6. Education and Learning Platforms
Edtech companies deploy real-time tutoring tools, grading automation, and adaptive learning systems to personalize student experiences.
7. Web3 and Blockchain
Projects in the decentralized space use intelligent agents to monitor smart contracts, analyze on-chain activity, and support token operations at scale.
Build With Experts Who Understand AI as a Service
If you are planning to integrate intelligence into your product, working with a team that understands both the strategy and the systems behind AI as a Service can save you time and help you scale without risk.
We specialize in:
- Custom AI assistant development tailored to specific industries
- Scalable models that grow with your business
- Full integration support across leading platforms
- Subscription-based access to tools you can rent, adapt, or own
Teams use our systems to power a wide range of applications, including e-commerce personalization, financial automation, wellness platforms, travel planning, and education services. No matter the use case, we help bring the idea to life with speed and reliability.
If you’re exploring AI as a service or already planning to adopt it in your product stack, our AI development services are here to support the build. Let’s talk about what you need and how we can help.
Closing Thoughts
AI as a service for businesses is no longer just a new idea. It’s becoming a key part of how modern products are built. AI as a service Companies that adopt it early can move faster, improve user experiences, and grow without the burden of complex AI development.
With the right tools and the right partner, intelligence can be built in, not bolted on. If you are exploring smarter systems for your next product or upgrade, this is the time to act. The future of AI as a service is here AI as a service makes it possible. Ment Tech Labs makes it real.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is AI as a Service (AIaaS)?
AI as a Service is a cloud-based model that allows businesses to use intelligent tools without building them from scratch. It offers AI cloud services like text analysis, image recognition, and forecasting through flexible subscription platforms.
2. What is the role of data in AI software development?
Data is essential for training, improving, and validating intelligent systems. In AIaaS platforms, data helps fine-tune models to match real-world scenarios, making predictions and outputs more accurate for specific business needs.
3. How is AI as a Service different from building custom AI?
Artificial Intelligence as a Service is faster to deploy and more affordable. It offers pre-trained models and APIs managed by providers. Custom AI development takes more time and resources but offers full control and customization.
4. Can small businesses use AI as a service?
Yes, small businesses can easily leverage AI services for business through AI as a Service. It offers cost-effective access to tools like chatbots, analytics, and automation without needing in-house infrastructure or expertise.
5. How does AI as a Service work?
AI as a Service (AIaaS) provides cloud-based AI tools that businesses can use without building their own infrastructure. It enables quick integration of AI like ML and NLP on a flexible, pay-as-you-go model