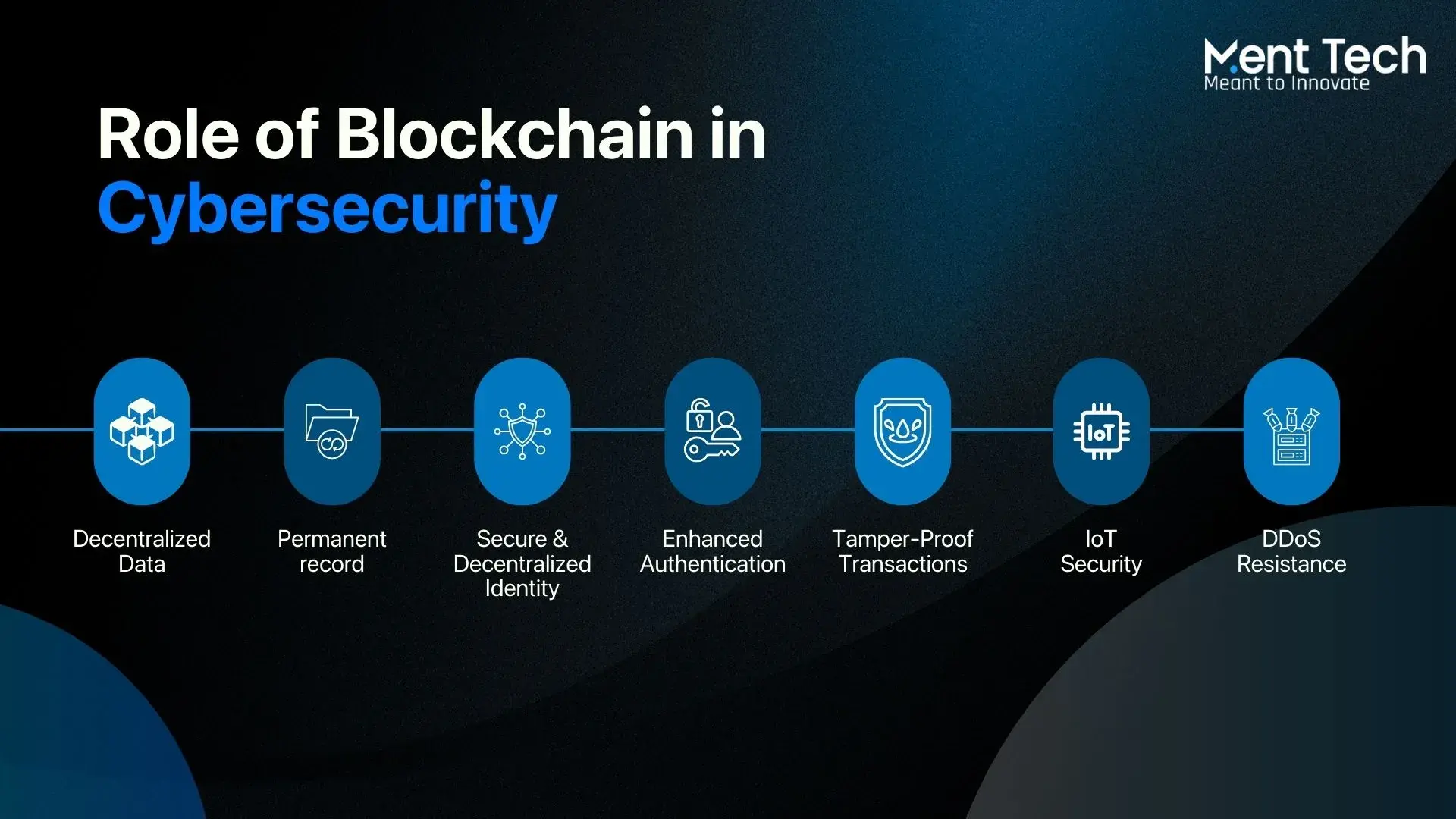
Cybersecurity keeps getting tougher for businesses and everyday users. Attacks are growing, data leaks are more common, and the cost of a single breach is rising every year. In the middle of all this, blockchain for cybersecurity is gaining new attention. A market that stood at $3.0B in 2024 is expected to grow to $37.4B by 2029, and another major forecast sees it reaching $176.6 by 2035. Growth like this doesn’t happen without strong demand, and it shows how quickly organizations are turning toward new ways to protect their systems.
At the same time, risks in the digital world are multiplying; illicit crypto activity alone touched ~$40.9B, highlighting how much stronger our defences need to be. More companies are now exploring how blockchain is used in cybersecurity as part of their security strategy, focusing on where it can add real protection and help reduce the impact of growing digital threats.
| Key Takeaways 1. Nearly 90% of businesses have either adopted or actively explored blockchain technology in cybersecurity, and approximately 86% of leaders believe it enhances efficiency and operational trust. 2. Around 45% of organizations have considered blockchain for cybersecurity, especially for safer data exchange and stronger encryption. 3. Cybercrime continues to drive security innovation, with global costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. 4. More than 50% of known blockchain cybersecurity risks scored 5.0 or higher on CVSS, and over 20% reached high to critical levels (7.0–10.0). |
What is Blockchain Security?
Blockchain security focuses on protecting digital data, systems, and transactions by spreading information across a shared network instead of storing it in one central place. Because data is verified and recorded by multiple connected systems, it becomes extremely difficult to change, steal, or manipulate. This approach has made blockchain in cybersecurity a trusted method for securing sensitive digital operations.
At Ment, we have successfully implemented these security principles for platforms like Aurix Exchange, where institutional-grade protection, data integrity, and risk control were essential. By using a distributed and transparent architecture, the platform ensures secure trading while reducing common blockchain cybersecurity risks without relying on a single controlling authority.
Common Tactics Fraudsters Use to Exploit Blockchain-Based Systems
Fraud in blockchain rarely starts with breaking the technology itself. Instead, attackers focus on users, platforms, and weak security layers around the network. As blockchain in cybersecurity becomes more common, understanding these attack paths is essential for reducing blockchain cybersecurity risks.
1. Social Engineering and Phishing
Fraudsters create fake emails, websites, and messages that look legitimate to trick users into sharing wallet keys or access details. This remains one of the biggest threats in blockchain for cybersecurity, as stolen access often leads to permanent loss of funds or data.
Real‑world example: Several users lost funds after interacting with fake OpenSea NFT sites that imitated the official platform to steal wallet credentials.
2. Investment and Ponzi Scams
Fake projects and unrealistic return promises are used to exploit trust. These scams are especially dangerous in blockchain and financial risk management, where users interact with blockchain for financial transactions without proper verification.
Real‑world example: The BitConnect platform collapsed, leaving investors with huge losses after operating as a Ponzi scheme under the guise of a cryptocurrency lending platform.
3. Smart Contract Exploits
Poorly tested contracts can contain logic gaps that attackers exploit to drain assets or manipulate outcomes. This exposes risks in blockchain applications in cybersecurity, particularly in decentralized finance platforms.
Real‑world example: The Poly Network suffered a smart contract exploit that allowed hackers to steal over $600 million in crypto assets, though much was later returned.
4. Wallet Malware and Device Takeovers
Malicious software can secretly monitor activity or steal private keys from user devices. This threat highlights why strong endpoint protection is essential in blockchain technology in cybersecurity.
Real‑world example: Users of MetaMask and Electrum wallets were targeted by malware that replaced copied wallet addresses with attacker-controlled ones, resulting in stolen funds.
5. Exchange and Platform Breaches
Centralized platforms hold large volumes of assets, making them attractive targets. When breached, attackers can access thousands of accounts at once, reinforcing the need for layered cybersecurity solutions with blockchain.
Real‑world example: The Binance exchange suffered a hack where attackers stole over $40 million worth of Bitcoin from user accounts, prompting enhanced security measures.
Why Businesses Switched to Blockchain for Cybersecurity?
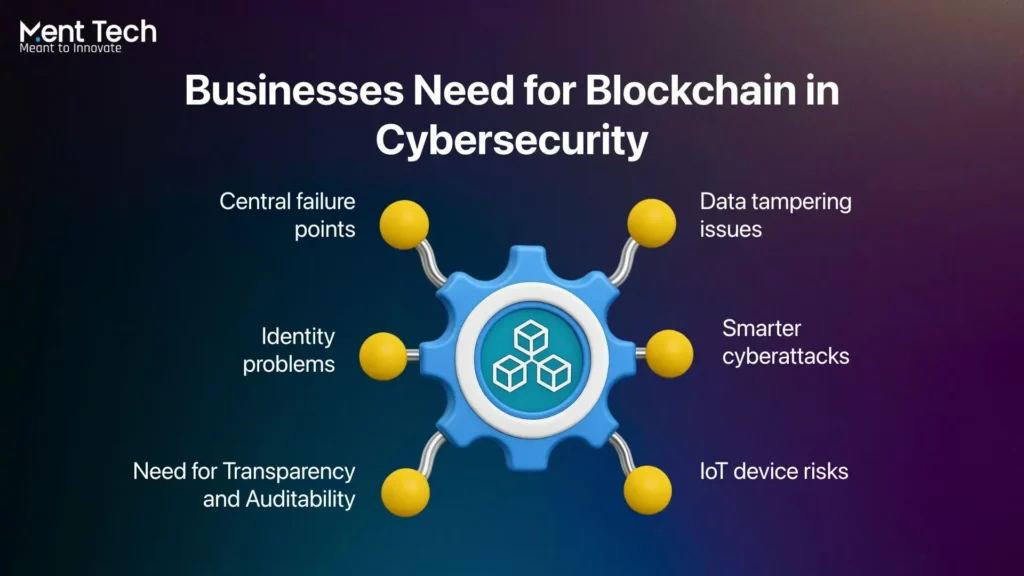
Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, revealing the limits of traditional security systems. Since a single breach can compromise everything, organizations are adopting blockchain-based cybersecurity and often work with blockchain development companies to create tailored, secure solutions.
Key Drivers for Blockchain in Cybersecurity.
- Central failure points: Most systems store all important data in one place, making it an easy target. Blockchain and cybersecurity solutions spread information across many nodes, removing the risk of “everything breaking at once.
- Data tampering issues: In regular setups, data can be quietly changed or deleted. Blockchain technology in cybersecurity ensures records cannot be altered once added, making tampering instantly visible.
- Identity problems: Passwords and traditional logins are often stolen. With cybersecurity solutions with blockchain, users can control their own digital identity without depending on a central database.
- Smarter cyberattacks: Ransomware, large-scale breaches, and system-wide attacks have shown that old methods don’t always hold up.
- Need for Transparency and Auditability: Industries like finance and healthcare need clean, tamper-proof records. The role of blockchain in cybersecurity provides a transparent trail that can’t be quietly changed.
- IoT device risks: Smart devices often have weak security. Blockchain applications in cybersecurity add safer ways for devices to communicate and verify each other.
As digital threats continue to grow and systems become increasingly connected, the weaknesses in traditional security are becoming increasingly impossible to ignore. Blockchain for cybersecurity may not solve everything, but it offers companies a fresh approach to protecting data and mitigating risks that older systems struggle to handle effectively.
How Blockchain Reduces Cyber Risk for Businesses?
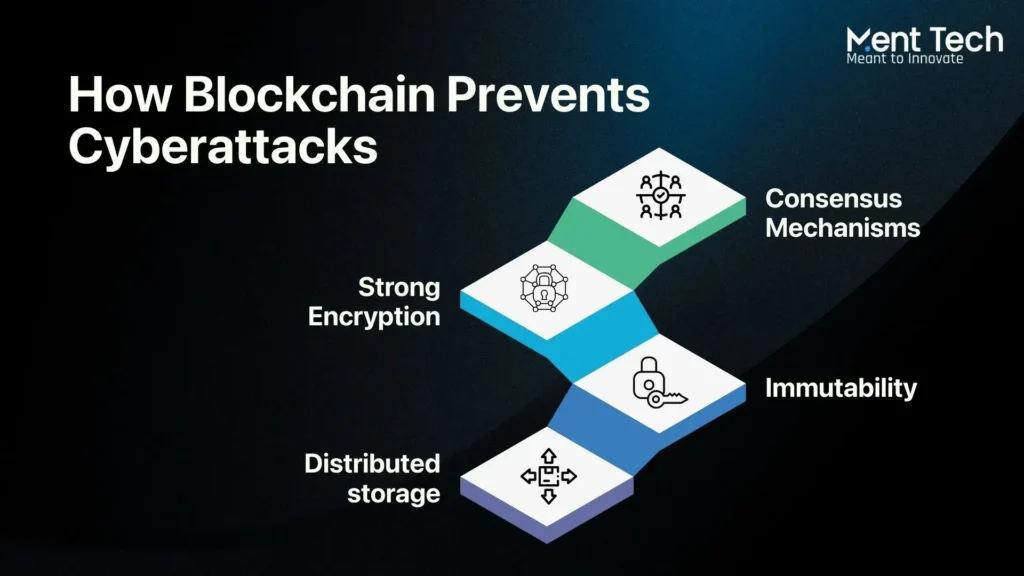
Blockchain improves security by storing data across multiple computers instead of a single system, making it harder for hackers to strike. Records are permanent and transparent, so any changes are immediately visible, and only authorized users can access sensitive information.
1. Distributed storage: Data is shared across multiple computers instead of being stored in a single server. This means even if one node is attacked or fails, the rest of the network keeps running safely, making large-scale breaches much harder.
2. Immutability: Once information is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or removed without approval from the majority of the network. This permanent record ensures transparency and accountability, demonstrating the role of blockchain in cybersecurity for trusted operations.
3. Strong Encryption: Blockchain uses advanced encryption to keep data safe. Only users with the correct keys can access or modify information, preventing unauthorized access and supporting cybersecurity solutions with blockchain.
4. Consensus Mechanisms: Every new entry or transaction is checked by multiple participants before being accepted. This collective process prevents fraud and tampering, showing how blockchain is used in cybersecurity to secure sensitive information.
Blockchain Use Cases in Cybersecurity
As cyber threats become more advanced, blockchain applications in cybersecurity help protect data and systems by improving security and trust. To build and audit these solutions effectively, many organizations hire blockchain developers with expertise in both distributed ledgers and threat prevention.
1. Secure Digital Identities:
Blockchain lets users control their own digital identities. Cryptographic keys replace passwords, reducing the risk of identity theft and ensuring only authorized people can access sensitive information.
2. Safe Data Storage and Sharing:
Instead of storing data in one central place, blockchain spreads it across multiple computers. Strong encryption protects data in transit, making blockchain technology in cybersecurity crucial for secure communication.
3. IoT Security:
Many smart devices have weak security. Blockchain helps devices authenticate themselves, manage keys, and make independent security checks, removing the risk of a single point of failure.
4. Supply Chain Security:
Blockchain tracks products from origin to delivery in a transparent and unchangeable way. This ensures product authenticity, protects data integrity, and holds everyone in the chain accountable.
5. DDoS and DNS Protection:
Traditional DNS systems can be overloaded by attacks. Blockchain decentralizes domain management, removing single points of failure and making it harder for attacks, highlighting blockchain and cybersecurity synergy.
6. Threat Alerts:
Blockchain enables secure and transparent sharing of threat data between organizations. This helps the cybersecurity community work together, respond faster to threats, and trust the information being shared.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain in Cybersecurity
Blockchain offers strong security benefits, but it also comes with trade-offs that can affect performance, cost, and usability. Knowing both sides helps organizations make smarter decisions before adopting it for cybersecurity.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
| Data Security | Information is spread across multiple nodes, reducing single points of failure. | Some blockchains process transactions slowly, limiting high-volume use. |
| Record Integrity | Once data is added, it can’t be changed, ensuring trustworthy records. | Mistakes or unwanted data can’t easily be removed. |
| Privacy & Access | Users can interact without revealing real identities; strong encryption keeps data safe. | Losing private keys means permanent loss of access. |
| Transparency & Accountability | Transactions are traceable and visible to authorized users. | Rules and regulations are still evolving, creating uncertainty. |
| Automation & Accuracy | Network verification reduces human errors and fraud. | Setup can be complex and requires technical expertise. |
| Environmental Impact | Some newer blockchain methods (e.g., proof-of-stake) are energy efficient. | Certain consensus methods consume a lot of electricity and resources. |
Real-World Blockchain Applications in Cybersecurity
Real-world examples show the tangible impact of blockchain on cybersecurity. They highlight how companies and governments are protecting data, preventing fraud, and securing critical systems, proving the technology’s practical value.
1. Veramo & Serto– Decentralized Identity Management
Veramo allows users to create and control their own digital identities without relying on a central authority. By using blockchain-based identifiers it reduces the risk of identity theft and ensures personal data stays secure while giving users full control over who accesses it.
2. Philips Healthcare– Securing Patient Records
Philips Healthcare uses blockchain to manage and protect sensitive medical data across hospitals and clinics. The system creates an immutable audit trail for patient records, allowing only authorized personnel to access information while improving transparency and trust.
3. IBM Watson IoT Platform– IoT Device Security
IBM integrates blockchain with its IoT platform to secure communication between connected devices. Device authentication, encrypted data sharing, and decentralized verification help prevent hacks and ensure the integrity of IoT networks.
4. Walmart (IBM Food Trust)—Supply Chain Security
Walmart uses blockchain to track food products from origin to store shelves. The technology provides full traceability, reduces fraud, ensures product authenticity, and allows rapid responses to contamination or other supply chain issues.
5. Barclays – Secure Fund Transfers
Barclays leverages blockchain to improve the security of fund transfers and customer information storage, demonstrating blockchain and financial risk management in real banking operations. By using distributed ledger technology, the bank strengthens transaction safety, reduces risks of fraud, and enhances trust in digital banking operations.

Future of Blockchain Cybersecurity
Blockchain is increasingly being combined with AI to provide smarter, real-time threat detection. Companies are already using decentralized networks to monitor unusual activity and stop attacks faster than traditional systems. Privacy-focused solutions, like zero-knowledge proofs, are being adopted to protect sensitive data without compromising transparency. Industries from healthcare to finance are exploring these hybrid approaches to make cybersecurity more proactive and resilient.
Interoperability between blockchain networks is improving, allowing secure sharing across platforms. Quantum-resistant encryption is gaining attention, and blockchain financial services and identity systems are giving users more control over personal data while reducing fraud. Clearer regulatory frameworks and corporate adoption are creating a stronger foundation for blockchain to reliably secure digital systems.
Conclusion
Blockchain is proving to be a practical tool for improving cybersecurity. By distributing data, protecting digital identities, securing IoT networks, and providing tamper-proof records, it addresses many weaknesses of traditional systems. Real-world examples across healthcare, finance, and supply chains show how these solutions reduce fraud, prevent attacks, and increase trust in digital systems.
At Ment Tech, we help you put blockchain to work in your cybersecurity strategy. We set up secure identity systems, monitor critical data, and protect devices across your network. By handling the security side, we let you focus on running your business with confidence, knowing your systems are safe and reliable.
FAQs
Blockchain is highly secure due to its decentralized and encrypted structure, but no system is 100% foolproof. Risks like private key loss or smart contract vulnerabilities still exist.
Blockchain complements rather than replaces existing security measures. It strengthens data integrity, identity management, and transaction security alongside traditional systems.
Ment Tech can implement blockchain-based identity systems, secure sensitive data, and monitor networks to protect businesses from cyber threats effectively.
Costs vary depending on scale, network type, and features. Small implementations can be affordable, while enterprise-level deployments may require significant investment.
When combined with AI or monitoring tools, blockchain can enable near real-time detection of unusual activity, helping prevent or limit damage.